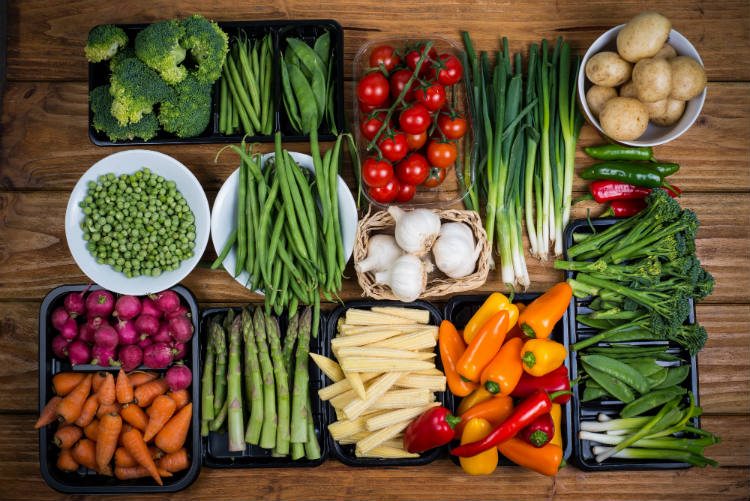
Most people are increasingly beginning to realize that foods that offer dietary fiber and probiotics have a long list of health benefits, yet prebiotic sources are still underestimated.

Generally, it has not consumed enough antibiotics daily and unfortunately has negative effects on our organism, such as indigestion, higher levels of inflammation, lower immune function, greater likelihood of regurgitation, and increased risk of various chronic diseases.
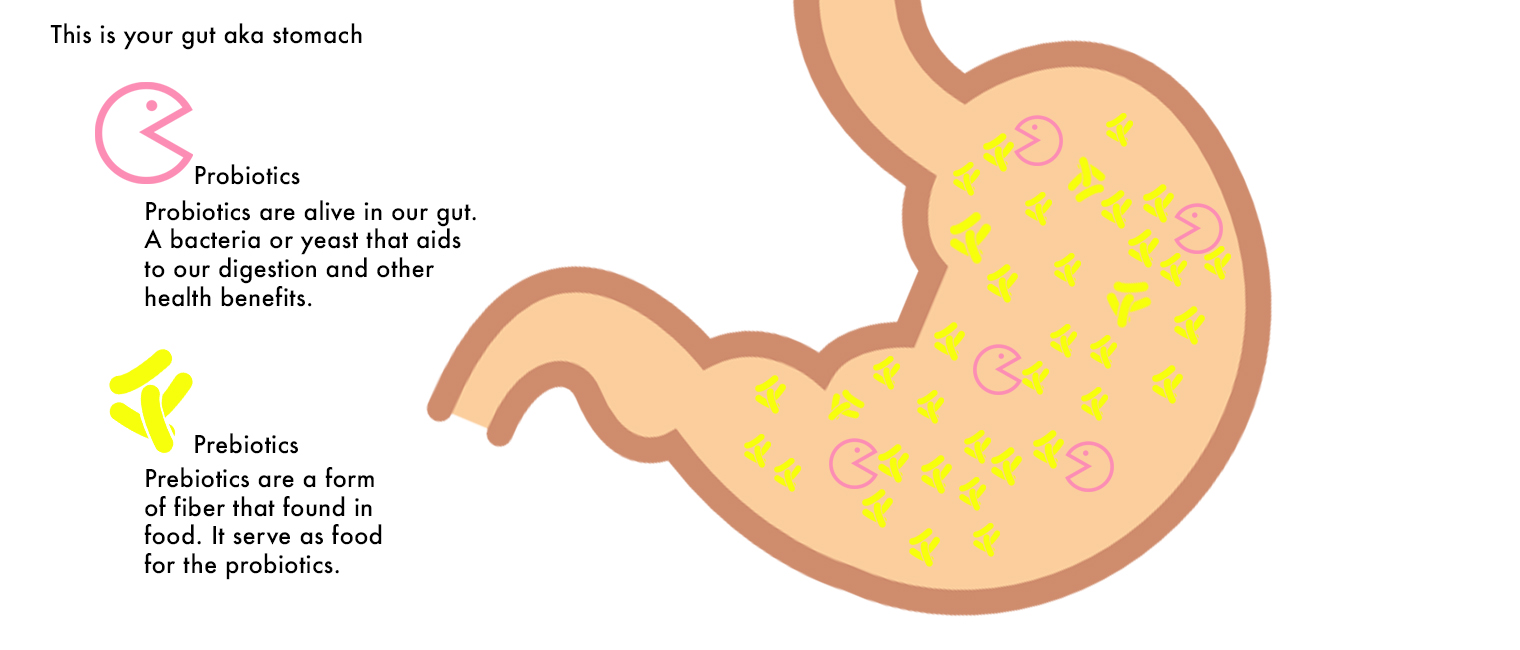
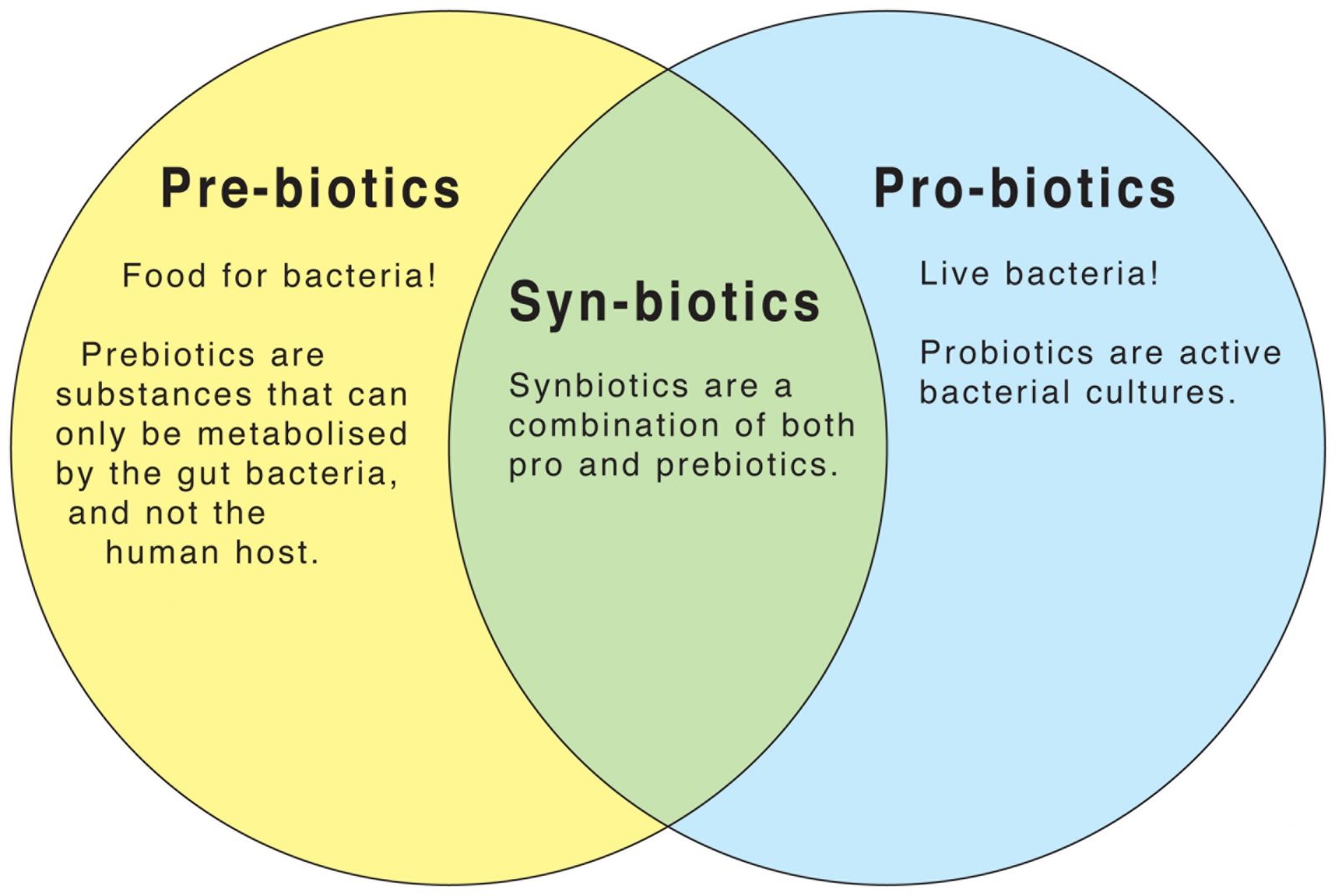
Prebiotics, also known as oligosaccharides, are carbohydrates that can not be "bruised" by the human organism. Together with the probiotics, they are responsible for maintaining a healthy digestive system.
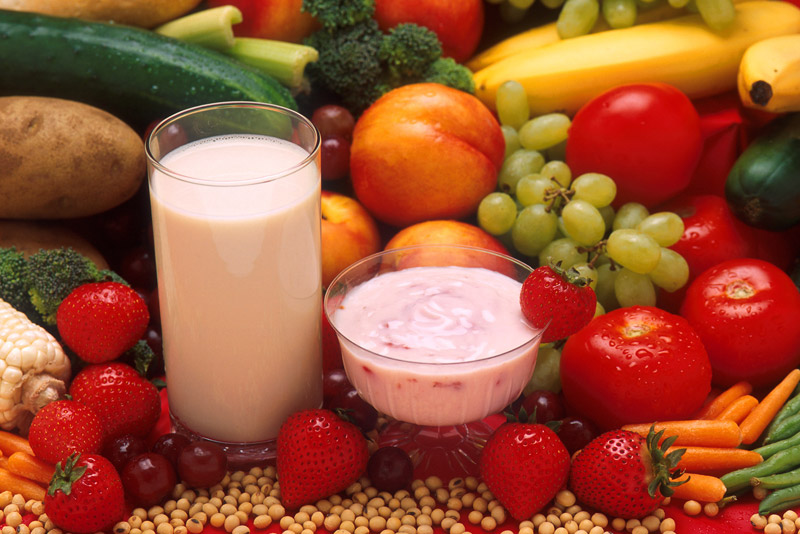
While the probiotic benefits have gained a lot of popularity in recent years, especially with the increased consumption of fermented foods, such as cabbage, kombucha, and kimchi, prebiotics are still in the background.
All types of fiber we eat from eating whole foods play an important role in the absorption of nutrients, intestines, and digestion. Prebiotics, along with probiotics, open the door for increased levels of health as a whole, so almost everyone can afford to include them in their diet more often.
Since prebiotics break through the stomach without decomposing either stomach acids or digestive enzymes, they lead to positive changes in the digestive tract and organs. In essence, prebiotic compounds become sources of nutrients or "fuel" for beneficial bacteria that live in your gut.
Prebiotics work together with probiotics (selectively fermented ingredients that produce beneficial bacteria) to allow for specific changes in both the composition and the activity of the gastrointestinal system. They play a key role in preserving health by maintaining the balance and variety of intestinal bacteria, especially by increasing the presence of "good bacteria," called lactobacilli and bifidobacteria.
Since bowel health is closely related to many other body functions, prebiotics and probiotics are together important to combat inflammation and reduce the overall risk of illness.
The main health benefits of prebiotics can be reduced to the following:
1. Maintain bowel health and improve digestion - stimulate the growth of beneficial bacteria that colonize the intestinal microflora and feed the probiotics. Prebiotic compounds help to balance harmful bacteria and toxins living in the digestive tract, which has many health implications, including improved digestion.

Changes in the composition of the intestinal microflora are classically considered one of the many factors involved in the development of inflammatory bowel disease or irritable bowel syndrome.
2. Improved immune function and cancer protection - A large number of human intervention studies have shown that the dietary consumption of some prebiotic-containing food products may result in statistically significant changes in the composition of the intestinal microflora that help improve immunity. reduce the concentration of some enzymes that stimulate cancer; prevents urinary tract infections.
Prebiotics help improves stool quality (frequency and consistency), reduce the risk of gastroenteritis and infections, improve overall well-being and reduce the incidence of allergic symptoms.

3. Reduce inflammation - they contribute to improving metabolic processes that are associated with both obesity and type 2 diabetes. The health of the intestine excludes autoimmune reactions, helps the body metabolize nutrients, including fats, and modulates hormonal and immune functions that control how and where the body stores fat.
4. Reduced risk of heart disease - Consuming foods high in prebiotics can reduce glycation, which increases free radicals, causes inflammation and lowers insulin resistance.
Prebiotics has the so-called hypo-cholesterolemic effect, improving the body's ability to prevent ischemic heart disease and autoimmune diseases (eg arthritis).

Another advantage is that they balance body electrolyte and mineral levels, including potassium and sodium, which are responsible for controlling blood pressure.
5. Weight loss - The latest data from human and animal studies support the beneficial effects of certain prebiotic food products with better homeostasis, saturation control, and lower body weight.
Higher quantities of all types of fibers are actually associated with lower body weight and obesity protection.

End of part 1..








Deja tu consulta/Leave your query Cancel Reply